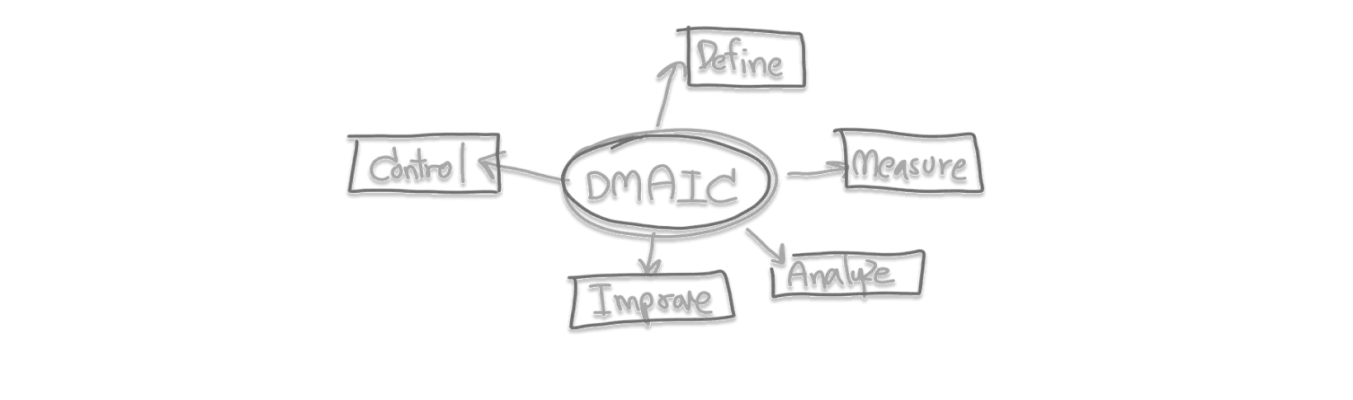
The DMAIC method is an integral part of the Six Sigma method, it is intended for successful management of the process leading to continuous improvement. This is an advanced PDCA cycle. The method is defined by five phases for successfully implementing change leading to improvement:
Define: The first phase involving defining objectives, gathering information and describing the state to be achieved. A team of workers is defined. The way in which the goal is to be achieved is not part of the definition, but the goal itself is defined.
Measure: Documenting the step-by-step steps leading to the set goal is a key factor. The gradual fulfillment of the goal can be documented according to predefined measurements and indicators. The measurement phase aims to collect and evaluate data on the current situation (occurrence of defects, recording of inputs and outputs).
Analyze: The information found in the previous step must be analyzed and the potential for improvement evaluated. The goal is to find out the critical factors that have a major influence on the occurrence of defects.
Improve: Eliminating the real cause of defects, establishing new processes and optimizing existing processes with the aim of optimizing input costs and increasing customer satisfaction.
Control: If the cause of the problem is correctly evaluated, the processes are successfully set and the improvement is achieved, the resulting changes must be implemented and standardized. Part of the final phase is monitoring the results achieved in a certain period and ensuring the permanent maintenance of the new state.